Compared With European-american Infants, Chinese and Japanese Babies Tend to Be __________.
Diana Baumrind's Parenting Styles Theory | Statistics | Infographic | Definition and Furnishings on Kids | The Most Effective Parenting Style | Nature vs Nurture | Quiz
What Is A Parenting Style?
The parenting styles commonly used in psychology today are based on the work of psychologist Diana Baumrind, a developmental psychologist at the Academy of California at Berkeley, in the 1960s. Maccoby and Martin besides contributed by refining the model in the 1980s.
Diana Baumrind's Parenting Styles Theory
Baumrind noticed that preschoolers exhibited distinctly different types of behavior. Each type of behavior was highly correlated to a specific kind of parenting.
Baumrind's theory is that there is a close relationship between the type of parenting fashion and children's behavior. Different styles of parenting tin pb to different child evolution and child outcomes.
Based on extensive observation, interviews, and analyses, Baumrind initially identified these iii parenting styles: administrative parenting, authoritarian parenting, and permissive parenting 1 .

Although Diana Baumrind is known for her piece of work on categorizing parenting styles, Maccoby and Martin (1983) were the ones who expanded this 3-parenting-styles model using a two-dimensional framework two .
They expanded Baumrind'southward permissive parenting way into two dissimilar types: permissive manner (also known as indulgent parenting manner) and neglectful parenting (likewise known equally uninvolved parenting style).
These iv parenting styles are sometimes called the Diana Baumrind parenting styles or Maccoby and Martin parenting styles.
The 4 types of parenting styles are:
- Authoritative
- Authoritarian (or Authoritarian)
- Permissive (or Indulgent)
- Neglectful (or Uninvolved)
Statistics on Parenting Styles
In the United states of america, roughly 46% of parents use authoritative parenting manner, 26% authoritarian parenting style, 18% permissive parenting style, and 10% neglectful parenting style three .
The distribution is relatively stable within the population, except that European-American parents are about two% more likely to have an authoritative style, while Asian-American parents are 2% more likely to have an authoritarian style.
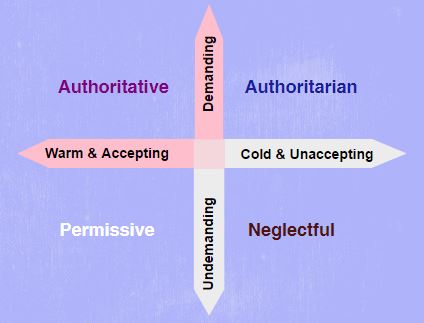
Parenting Styles Nautical chart Infographic

Parenting Styles Definition and Their Effects on Children's Behavior
Parenting styles are categorized based on two dimensions of parenting behavior and styles:
Demandingness refers to the extent to which parents control their child's behavior or demand their maturity.
Responsiveness refers to the degree to which parents are accepting and sensitive to their children's emotional and developmental needs.
Here are the impacts of parenting styles on child development.

1. Administrative Parenting
High demandingness. Loftier responsivenss.
Authoritative parents have high expectations for achievement and maturity, but they are as well warm and responsive four .
These parents gear up rules and enforce boundaries past having open discussions, providing guidance, and using reasoning.
These parents provide their kids with reasoning and explanation for their deportment. Explanations allow children to have a sense of sensation and teach kids almost values, morals, and goals.
Their disciplinary methods are confrontative 5 , i.e. reasoned, negotiable, outcome-oriented, and concerned with regulating behaviors.
Authoritative parents are appreciating and supportive. They respect their children's autonomy, provide them with a lot of freedom and encourage independence.
They as well allow bidirectional communication. This fashion of parenting is as well known as the democratic parenting manner 6 .
Children of authoritative parents are cherished.
Based on Baumrind'southward research on parenting styles, children of authoritative parents tend to 7 :
- Appear happy and content.
- Are more independent
- Are more than active viii .
- Achieve higher academic functioning 8–10 .
- Develop good self-esteem eleven .
- Interact with peers using competent social skills 12 .
- Take ameliorate mental wellness — less low, anxiety, suicide attempts, delinquency, booze and drug utilise 13–fifteen .
- Exhibit less violent tendencies 16 .
- Are deeply attached.

two. Disciplinarian Parenting
High demandingness. Low reponsiveness.
High levels of parental control and depression levels of parental responsiveness are the two characteristics of the authoritarian style.
Although authoritarian parenting and authoritative parenting styles have similar names, they have several important differences in parenting conventionalities, demand, and approach.
While both parental styles demand loftier standards, authoritarian parents need bullheaded obedience using reasons such every bit "because I said so". They only allow one-way communication through strict rules and orders. Whatever attempts to reason with them are seen as animadversion.
These parents use stern subject and often employ harsh punishment, such as corporal punishment, as a way to obtain behavioral command. Their disciplinary methods are coercive five , i.e. arbitrary, peremptory, domineering, and concerned with mark status distinctions.
Disciplinarian parents are unresponsive to their child'due south needs and are generally not nurturing. They usually justify using mean handling to toughen up their kids.
Children whose parents accept an authoritarian parenting mode tend to:
- Have an unhappy disposition.
- Exist less independent.
- Announced insecure.
- Possess low self-esteem.
- Showroom more than behavioral problems or deport issues 17 .
- More temper tantrums.
- Perform worse academically.
- Take poorer social competence.
- Exist more prone to mental bug eighteen .
- Be more likely to have drug use problems 19 .
- Have worse coping skills 20 .

iii. Permissive Parenting (Indulgent)
Low demandingness. High responsiveness
Permissive parents set up very few rules and boundaries and they are reluctant to enforce rules.
These indulgent parents are warm and indulgent only they practise not similar to say no or disappoint their children.
Children of permissive parents tend to have the worst outcomes:
- Cannot follow rules.
- Have worse cocky-control.
- Possess egocentric tendencies.
- Encounter more problems in relationships and social interactions.

4. Neglectful Parenting (Uninvolved)
Depression demandingness. Low responsiveness.
Neglectful parents do non set house boundaries or high standards.
They are indifferent to their children's needs and uninvolved in their lives.
These uninvolved parents may accept mental issues themselves such as low, physical abuse, or kid fail when they were kids.
Children of neglectful parents:
- Are more impulsive.
- Cannot self-regulate emotion.
- Encounter more delinquent beliefs and addictions issues.
- Have more mental issues — e.thou. suicidal beliefs in adolescents.

Which Parenting Manner Is The Most Effective?
From decades of studies, research shows that authoritative parenting is consistently linked to the best outcomes in kids.
The administrative parenting style is considered the best parenting style past psychologists and psychiatrists.
This classification of child rearing styles has been studied for over 25 years in different countries.
Results are mostly found to be every bit expected for each parenting mode.
Still, inconsistencies and exceptions in some areas remain.
Here are some important factors that may also play a role in determining how a kid turns out.
Cultural and Ethnics Differences
Some studies constitute that the authoritative style isn't always linked to the best schoolhouse achievement across families from diverse ethnic (due east.g. Asian, Black, Hispanic) and socioeconomic backgrounds (e.g. income level, parental educational activity, number of active parents) 21 .
For example, in one study, researchers plant that African-American students with authoritative parents merely without peer support did non perform the best academically.
As for Asian-American students, in some studies, they performed the best in school when they had authoritarian parents and peer support 22 .
In Spain, a report showed that both indulgent and authoritative parenting styles were associated with positive outcomes 23 .
Child Temperament
Children's ain behavior tin can affect the parent'southward selection and the outcomes, likewise.
For example, kids with a more than sensitive temperament may exist perceived every bit difficult causing the parents to change their parenting style towards more authoritarian.
In a study, it was too establish that some aspect of kid behavior such as sociable and aggressive behaviors are amend correlated to the child's temperament than to the parenting style of their parents.
It seems like parenting style is not the but determining cistron in the child'southward outcomes.
Differences in social context and in child temperaments can make a difference, as well.
But information technology is worth noting that, despite being widely publicized, not all of these study results have been successfully reproduced by other researchers.
In addition, these results are likewise not consistent across other types of outcomes, such equally behavior or mental health.
For example, while some studies constitute the use of authoritarian parenting in the Chinese American population was associated with the best bookish outcomes 24 , others found the administrative parenting to be the best in predicting school functioning 25 .
To this engagement, no study has conclusively disproved the benefits of authoritative parenting, while many others take consistently shown its advantages.
Authoritative parenting is still the about encouraged parenting style in modern America equally recommended past experts.
Parenting Styles vs Parenting Practices
Another component that can impact the result is the stardom betwixt parenting style and parenting do.
Parenting style is the emotional climate and control in which parents heighten their children.
Parenting practices are specific actions that parents utilize in their parenting.
Even for parents with the same parenting style, they may cull to dissimilar means or different approaches to implementing specific parenting practices and that will affect the degree of outcomes.
Limitations And Criticisms Of Parenting Studies
When interpreting research results, it is of import to annotation that nigh of these parenting studies just find links between parenting styles and outcomes.
That is, the results are only correlation and not causation.
For example, parents who are warm and responsive tend to have children who exhibit less behavior problems. I is tempted to say that therefore warm and responsive parents result in better behaving kids.
But yous can easily turn that effectually and say that kids who behave cause their parents to be more warm and responsive.
Different children have dissimilar temperaments and they can, in turn, touch on parents' behavior.
These parenting inquiry does non tell us which one is the correct cause-and-effect relationship.
So why practice virtually psychologists and experts nonetheless recommend authoritative parenting style?
One reason is that there are overwhelming volumes of studies showing these connections consistently.
Some other reason is that in that location is no enquiry that shows authoritative parenting style causes harm to children.
As a parent, if I take to cull one parenting mode, without any research data, I would consider my parenting goals and the type of parent I want to be.
My ultimate parenting goal is to raise a salubrious, happy, kind, and responsible person who will love me and our family when she grows up. AND I also want to enjoy the experience of parenting.
It is difficult to imagine being cold and strict (authoritarian), cold and indifferent (neglectful), or warm and indulgent (permissive) will achieve all of my goals.
The authoritative parenting style simply makes sense to me.
Which parenting way is most encouraged in modernistic America?
Of the four Baumrind parenting styles, the authoritative parenting style is the one that is most encouraged in modern American guild.
Also Run into: Montessori Parenting
Nature Vs Nurture

Nature vs nurture is ane of the oldest debates in the history of psychology. Which i matters more?
A contempo study by the Queensland Brain Institute and the VU University of Amsterdam has pretty much settled the Nature vs Nurture debate. 14.5 million pairs of twins from almost every twin study ever done in the by 50 years were collected and analyzed 26 .
Researchers accept found that a person'south behavior and character traits are influenced roughly the same by genetics (nature) and past environment (nurture).
Parenting is one of the most important parts of the environment a child is exposed to since birth. Good parenting'due south impact on a child is significant and undeniable.
Likewise See: How Does The Decease Of A Parent Affect A Child
Parenting Style Quiz
To find out your parenting fashion, try this test at PsychCentral.
References
-
2.
Maccoby EE, Martin JA. Socialization in the Context of the Family: Parent-Child Interaction. In: Handbook of Child Psychology. Socialization, Personality, and Social Development. ; 1983:.
-
three.
Pong South ling, Johnston J, Chen 5. Disciplinarian Parenting and Asian Adolescent School Performance: Insights from the US and Taiwan. International Journal of Behavioral Evolution. Published online November 6, 2009:62-72. doi:ten.1177/0165025409345073
-
4.
Darling N, Steinberg L. Parenting fashion every bit context: An integrative model. Psychological Bulletin. 1993;113(39):487-496.
-
5.
Baumrind D. Differentiating betwixt Confrontive and Coercive Kinds of Parental Ability-Assertive Disciplinary Practices. Human Evolution. Published online 2012:35-51. doi:10.1159/000337962
-
half dozen.
Miklikowska M, Hurme H. Democracy begins at home: Democratic parenting and adolescents' support for democratic values. European Journal of Developmental Psychology. Published online June 28, 2011:541-557. doi:x.1080/17405629.2011.576856
-
vii.
Steinberg Fifty, Lamborn SD, Dornbusch SM, Darling North. Impact of Parenting Practices on Adolescent Achievement: Authoritative Parenting, School Involvement, and Encouragement to Succeed. Kid Development. Published online Oct 1992:1266. doi:10.2307/1131532
-
8.
Spera C. A Review of the Relationship Among Parenting Practices, Parenting Styles, and Adolescent School Accomplishment. Educ Psychol Rev. Published online June 2005:125-146. doi:10.1007/s10648-005-3950-i
-
ix.
Nyarko K. The influence of authoritative parenting style on adolescents' academic achievement. AJSMS. Published online September 2011:278-282. doi:x.5251/ajsms.2011.2.3.278.282
-
10.
Strage A, Brandt TS. Administrative parenting and college students' bookish adjustment and success. Journal of Educational Psychology. Published online 1999:146-156. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.91.one.146
-
eleven.
McClun LA, Merrell KW. Relationship of perceived parenting styles, locus of control orientation, and cocky-concept among junior loftier age students. Psychol Schs. Published online Oct 1998:381-390. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1998-12495-009
-
12.
Rankin Williams L, Degnan KA, Perez-Edgar KE, et al. Impact of Behavioral Inhibition and Parenting Style on Internalizing and Externalizing Problems from Early Childhood through Adolescence. J Abnorm Child Psychol. Published online June 12, 2009:1063-1075. doi:10.1007/s10802-009-9331-3
-
13.
Rothrauff TC, Cooney TM, An JS. Remembered Parenting Styles and Adjustment in Centre and Late Adulthood. The Journals of Gerontology Serial B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences. Published online January 1, 2009:137-146. doi:10.1093/geronb/gbn008
-
14.
Newman K, Harrison Fifty, Dashiff C, Davies S. Relationships betwixt parenting styles and run a risk behaviors in adolescent health: an integrative literature review. Rev Latino-Am Enfermagem. Published online February 2008:142-150. doi:10.1590/s0104-11692008000100022
-
15.
Zeinali A, Sharifi H, Enayati M, Asgari P, Pasha G. The mediational pathway amongst parenting styles, attachment styles and self-regulation with addiction susceptibility of adolescents. J Res Med Sci. 2011;16(9):1105-1121. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22973379
-
16.
Jackson C, Henriksen L, Foshee VA. The Authoritative Parenting Index: Predicting Wellness Take chances Behaviors Among Children and Adolescents. Health Educ Behav. Published online June 1998:319-337. doi:10.1177/109019819802500307
-
17.
Smith JD, Dishion TJ, Shaw DS, Wilson MN, Wintertime CC, Patterson GR. Coercive family process and early-onset bear bug from age 2 to school entry. Dev Psychopathol. Published online Apr 2, 2014:917-932. doi:10.1017/s0954579414000169
-
xviii.
Martin G, Waite S. Parental bonding and vulnerability to adolescent suicide. Acta Psychiatr Scand. Published online April 1994:246-254. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1994.tb01509.x
-
19.
Baumrind D. The Influence of Parenting Style on Adolescent Competence and Substance Use. The Journal of Early Adolescence. Published online February 1991:56-95. doi:10.1177/0272431691111004
-
20.
Wolfradt U, Hempel S, Miles JNV. Perceived parenting styles, depersonalisation, feet and coping behaviour in adolescents. Personality and Individual Differences. Published online February 2003:521-532. doi:10.1016/s0191-8869(02)00092-ii
-
21.
Steinberg Fifty, Dornbusch S. Ethnic differences in adolescent achievement: An ecological perspective. American Psychologist. 1992;47(6):723-729.
-
22.
Chao RK. Beyond Parental Command and Authoritarian Parenting Style: Agreement Chinese Parenting Through the Cultural Notion of Training. Child Evolution. Published online August 1994:1111. doi:10.2307/1131308
-
23.
Garcia F, Gracia Eastward. Is ever administrative the optimum parenting fashion? Evidence from Spanish families. Adolescence. 2009;44(132):101.
-
24.
Chao RK. The Parenting of Immigrant Chinese and European American Mothers. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology. Published online March 2000:233-248. doi:10.1016/s0193-3973(99)00037-four
-
25.
Chen X, Dong Q, Zhou H. Authoritative and Authoritarian Parenting Practices and Social and School Performance in Chinese Children. International Journal of Behavioral Evolution. Published online November 1997:855-873. doi:ten.1080/016502597384703
-
26.
Polderman TJC, Benyamin B, de Leeuw CA, et al. Meta-analysis of the heritability of human traits based on l years of twin studies. Nat Genet. Published online May eighteen, 2015:702-709. doi:10.1038/ng.3285
Source: https://www.parentingforbrain.com/4-baumrind-parenting-styles/
0 Response to "Compared With European-american Infants, Chinese and Japanese Babies Tend to Be __________."
Post a Comment